14. VirtIO Net Library#
VirtIO-net library is the virtualization solution used in Marvell DPU platforms for networking. This model emulates SMART NICs for VM and front end virtio network driver, providing high-performance virtualized networking across multiple Marvell DPU architectures.
14.1. Features#
Currently, VirtIO emulation device supports VirtIO 1.2 specification, where it offers below features.
14.1.1. VirtIO Common Feature Bits:#
VIRTIO_F_RING_PACKED
VIRTIO_F_VERSION_1
VIRTIO_F_ANY_LAYOUT
VIRTIO_F_IN_ORDER
VIRTIO_F_ORDER_PLATFORM
VIRTIO_F_NOTIFICATION_DATA
14.1.2. VirtIO-net Feature Bits:#
VIRTIO_NET_F_CTRL_VQ
VIRTIO_NET_F_MQ
VIRTIO_NET_F_RSS
VIRTIO_NET_F_CTRL_RX
VIRTIO_NET_F_STATUS
VIRTIO_NET_F_MAC
VIRTIO_NET_F_MRG_RXBUF
VIRTIO_NET_F_CTRL_MAC_ADDR
VIRTIO_NET_F_CTRL_VLAN
VIRTIO_NET_F_CSUM
VIRTIO_NET_F_GUEST_CSUM
VIRTIO_NET_F_MTU
VIRTIO_NET_F_HASH_REPORT
VIRTIO_NET_F_HOST_TSO4
VIRTIO_NET_F_HOST_TSO6
VIRTIO_NET_F_GUEST_HDRLEN
Here are some notes about VirtIO-net features:
Modern devices are supported, legacy devices are not supported.
Only Packed virtqueues(VIRTIO_F_RING_PACKED) are supported.
Use the buffers in the same order in which they have been made available(VIRTIO_F_IN_ORDER).
Expects extra data(besides identifying the virtqueue) in device notifications( VIRTIO_F_NOTIFICATION_DATA). This is a mandatory feature to be enabled by Host/Guest.
Using VIRTIO_F_ORDER_PLATFORM is mandatory for proper functioning of smart NIC as it ensures memory ordering between Host and DPU.
14.2. Platform Support#
The VirtIO net library supports multiple Marvell DPU platforms:
CN10K platforms: Uses capability BAR 4 for VirtIO device configuration
Structera platforms: Uses capability BAR 1 for VirtIO device configuration
The platform-specific configuration is detected automatically at runtime through the PEM platform detection mechanism.
14.3. VirtIO Emulation Architecture Overview#
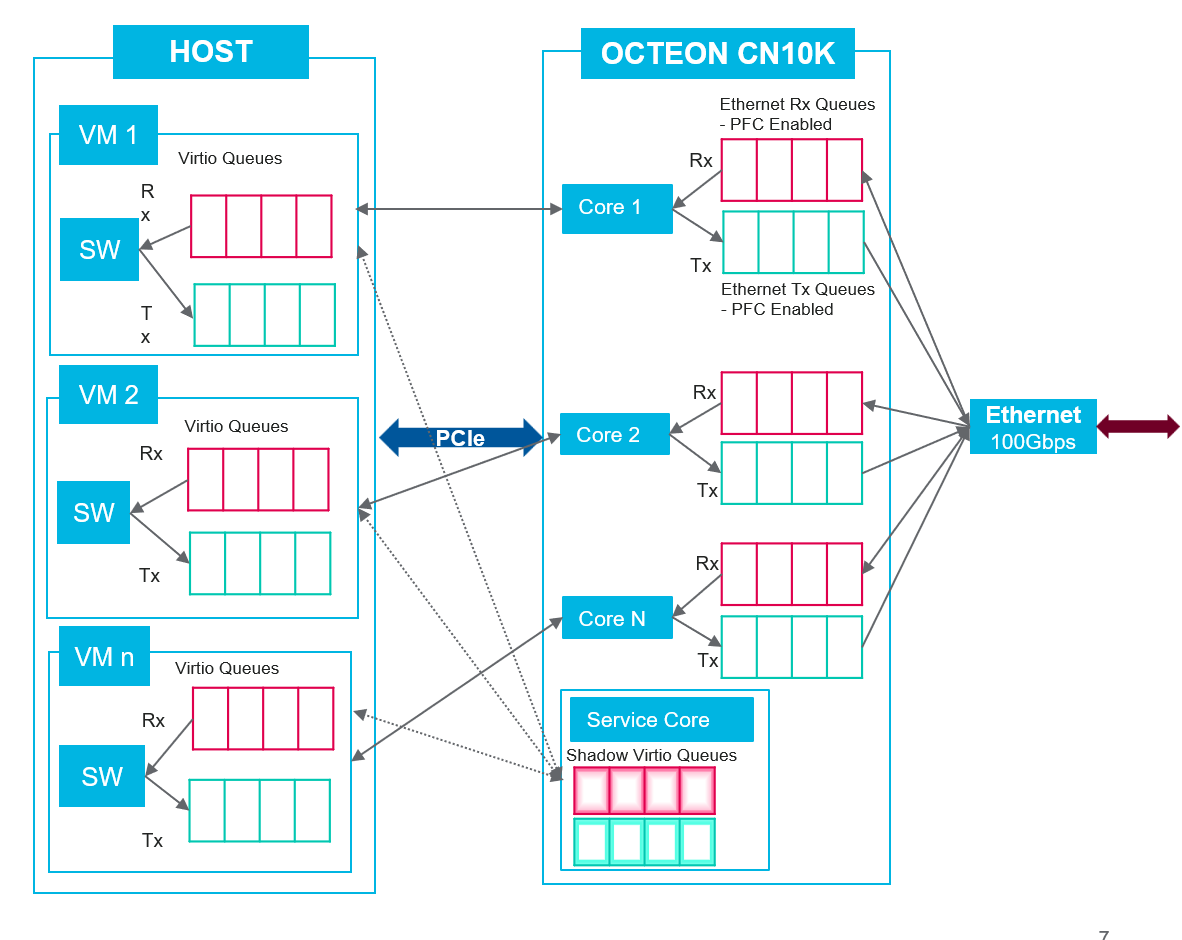
This design fosters a scalable architecture with an emulation software core serving two crucial roles: the service core and worker core.
The service core acts as the overseer, managing the virtio queue descriptors exchanged between the host and FW. Its responsibilities include determining the queue depth, tracking head and tail pointers, and marking buffers as available or in-use. Meanwhile, the worker cores leverage the services provided by the service core, effectively facilitating the movement of packets between the host and FW.
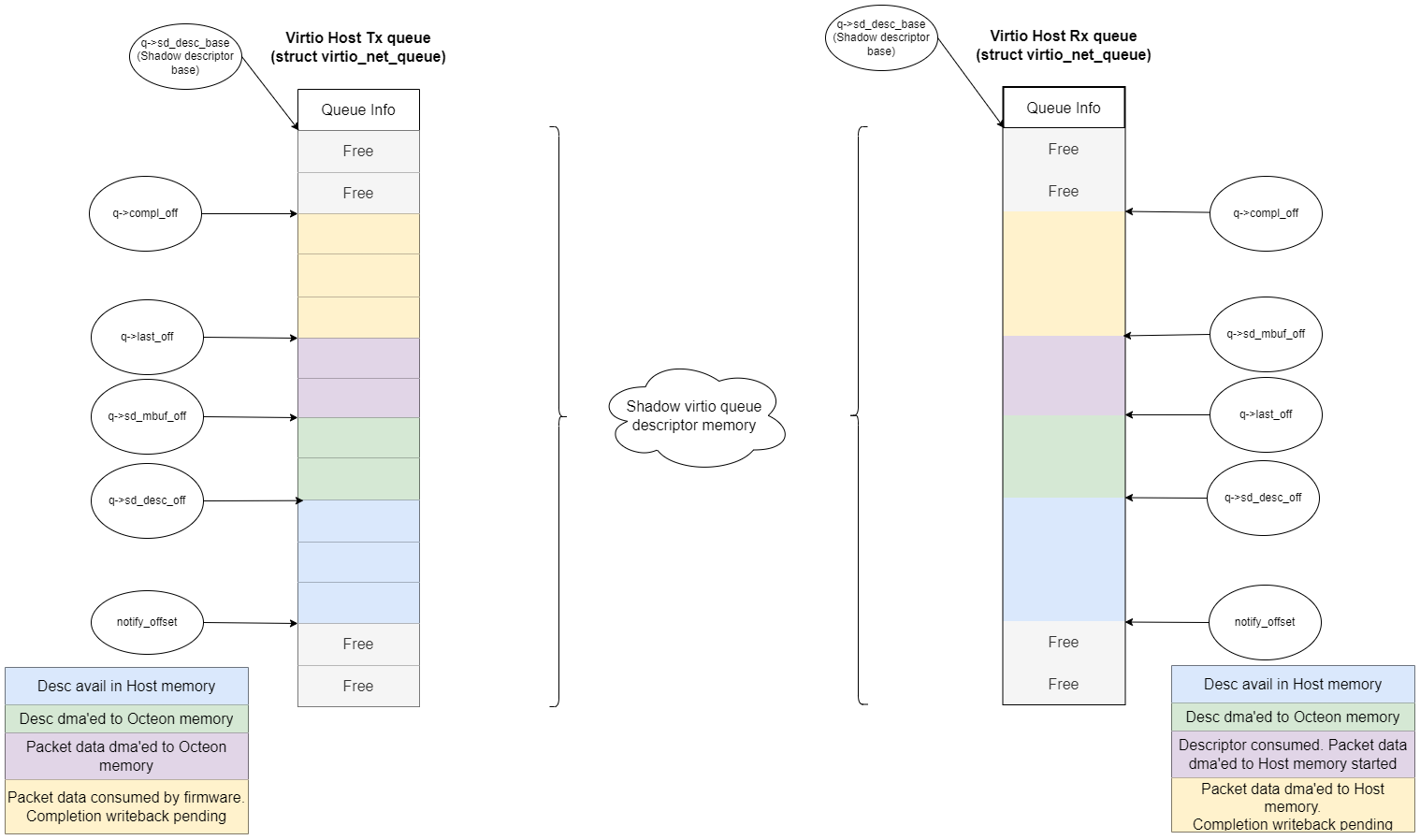
Internally the above figure depicts virtio-net library architecture. Each portion of descriptor
area follows several stages of processing one after the other. The process is triggered by
notification data update to move the tail/avail index to end of available descriptors.
This triggers service core calling dao_virtio_netdev_desc_manage() to initiate a DMA fetch of
descriptor data. As depicted in the figure, q->sd_desc_off follows notify_offset,
q->sd_mbuf_off in dequeue queue follows q->sd_desc_off while in enqueue queue,
q->last_off follows q->sd_desc_off and soon.
Once descriptor data is fetched, the service core updates q->sd_desc_off so that worker cores
can process the descriptors and then further initiate Packet data transfer between Host packet buf
and DPU DPDK mbuf memory.
Once the worker cores have consumed a descriptor data, they move q->last_off for
dequeue queue(Host Tx queue) or q->sd_mbuf_off for enqueue queue(Host Rx queue) in local data
structure so that service core via dao_virtio_netdev_desc_manage() takes that info and
pushes descriptor updates from shadow memory back to Host descriptor ring. Basically number of
descriptors to mark complete is nothing but the distance between q->compl_off and the
next offset i.e q->last_off or q->sd_mbuf_off.
14.4. VirtIO-net device identification#
Each virtio net device is designated by a unique device index starts from 0, in all functions. Currently, this library supports maximum of 64 virtio net devices, one to one mapped to a PEM VF. VirtIO devid[11:0] indicates VF number while devid[15:12] indicates PF number within that VF. A virtio device is always connected to Host VF. Host PF doesn’t have a virtio device representation in the library.
14.5. Device initialization#
The initialization of each virtio net device includes the following operations:
Initialize base virtio device using
virtio_dev_init()API, which populates the virtio capabilities to be available to host.Populates default values to
struct virtio_net_config.
The dao_virtio_netdev_init() API is used to initialize a VirtIO net device.
int dao_virtio_netdev_init(uint16_t devid, struct dao_virtio_netdev_conf *conf)
The dao_virtio_netdev_conf structure is used to pass the configuration parameters shown below.
struct dao_virtio_netdev_conf {
/** PEM device ID */
uint16_t pem_devid;
/** Config flags */
#define DAO_VIRTIO_NETDEV_EXTBUF DAO_BIT_ULL(0)
uint16_t flags;
union {
struct {
/** Default dequeue mempool */
struct rte_mempool *pool;
};
/** Valid when DOS_VIRTIO_NETDEV_EXTBUF is set in flags */
struct {
uint16_t dataroom_size;
};
};
/** Vchan to use for this virtio dev */
uint16_t dma_vchan;
/** Max virt_queue pairs limit */
uint16_t max_virt_qps_limit;
/** Auto free enabled/disabled */
bool auto_free_en;
/** RETA size supported */
uint16_t reta_size;
/** HASH key size supported */
uint16_t hash_key_size;
/** Default MTU */
uint16_t mtu;
/** Default MAC address */
uint8_t mac[VIRTIO_NET_ETHER_ADDR_LEN];
/** Link info */
struct dao_virtio_netdev_link_info link_info;
/** Enable/disable checksum offload feature */
bool csum_en;
};
The application virtio-l2fwd is a sample application that shows how to use virtio net library.
Sample code to set dao_virtio_netdev_conf parameters:
/* Populate netdev conf */
memset(&netdev_conf, 0, sizeof(netdev_conf));
netdev_conf.auto_free_en = virtio_netdev_autofree;
netdev_conf.pem_devid = pem_devid;
netdev_conf.pool = per_port_pool ? v_pktmbuf_pool[virtio_devid] : v_pktmbuf_pool[0];
netdev_conf.dma_vchan = virtio_netdev_dma_vchans[virtio_devid];
netdev_conf.mtu = 0;
if (virtio_map[virtio_devid].type == ETHDEV_NEXT) {
struct rte_eth_link eth_link;
portid = virtio_map[virtio_devid].id;
netdev_conf.reta_size = eth_dev_info[portid].reta_size;
netdev_conf.hash_key_size = eth_dev_info[portid].hash_key_size;
overhd = eth_dev_get_overhead_len(eth_dev_info[portid].max_rx_pktlen,
eth_dev_info[portid].max_mtu);
rte_eth_link_get(portid, ð_link);
netdev_conf.link_info.status = eth_link.link_status;
netdev_conf.link_info.speed = eth_link.link_speed;
netdev_conf.link_info.duplex = eth_link.link_duplex;
/* Register link status change interrupt callback */
rte_eth_dev_callback_register(portid, RTE_ETH_EVENT_INTR_LSC,
lsc_event_callback,
(void *)(uint64_t)virtio_devid);
/* Populate default mac address */
rte_eth_macaddr_get(portid, (struct rte_ether_addr *)netdev_conf.mac);
} else {
netdev_conf.reta_size = 128;
netdev_conf.hash_key_size = 48;
/* Link status always UP */
netdev_conf.link_info.status = 0x1;
netdev_conf.link_info.speed = RTE_ETH_SPEED_NUM_UNKNOWN;
netdev_conf.link_info.duplex = 0xFF;
}
if (max_pkt_len)
netdev_conf.mtu = (max_pkt_len - overhd);
netdev_conf.auto_free_en = virtio_netdev_autofree;
/* Save reta size for future use */
virtio_netdev_reta_sz[virtio_devid] = netdev_conf.reta_size;
/* Initialize virtio net device */
rc = dao_virtio_netdev_init(virtio_devid, &netdev_conf);
if (rc)
rte_exit(EXIT_FAILURE, "Failed to init virtio device\n");
14.6. User callback APIs#
The application is expected to register callbacks to take the appropriate actions for each control command. VirtIO net library triggers the corresponding callback function when it receives the control command.
The API dao_virtio_netdev_cb_register is used to register the user callback APIs.
void dao_virtio_netdev_cb_register(struct dao_virtio_netdev_cbs);
The dao_virtio_netdev_cbs structure is used to pass the cbs. The following callbacks can be registered currently,
struct dao_virtio_netdev_cbs {
/** Device status callback */
dao_virtio_netdev_status_cb_t status_cb;
/** RSS setup callback */
dao_virtio_netdev_rss_cb_t rss_cb;
/** Promisc mode callback */
dao_virtio_netdev_promisc_cb_t promisc_cb;
/** All multi callback */
dao_virtio_netdev_allmulti_cb_t allmulti_cb;
/** Mac set callback */
dao_virtio_netdev_mac_set_cb_t mac_set;
/** Mac filter callback */
dao_virtio_netdev_mac_add_cb_t mac_add;
/** Multi queue configure callback */
dao_virtio_netdev_mq_cfg_t mq_configure;
/** VLAN filter add callback */
dao_virtio_netdev_vlan_t vlan_add;
/** VLAN filter del callback */
dao_virtio_netdev_vlan_t vlan_del;
/** Alloc extbuf */
dao_virtio_netdev_extbuf_get extbuf_get;
/** Free extbuf */
dao_virtio_netdev_extbuf_put extbuf_put;
};
14.7. Queue count#
Application is expected to get the active virt queues count using dao_virtio_netdev_queue_count and equally distribute the rx and tx queues among all the subscribed lcores.
14.8. Link status update#
The API dao_virtio_netdev_link_sts_update is used to update the virtio net port
link info in virtio_net_config to be available to host. Below is same code to update
netdev link status through DPDK lsc event callback.
static int
lsc_event_callback(uint16_t port_id, enum rte_eth_event_type type __rte_unused, void *param,
void *ret_param __rte_unused)
{
struct dao_virtio_netdev_link_info link_info;
uint16_t virtio_devid = (uint64_t)param;
struct rte_eth_link eth_link;
rte_eth_link_get(port_id, ð_link);
link_info.status = eth_link.link_status;
link_info.speed = eth_link.link_speed;
link_info.duplex = eth_link.link_duplex;
dao_virtio_netdev_link_sts_update(virtio_devid, &link_info);
return 0;
}
14.9. VirtIO descriptors Management API#
The virtio net library provides an API for managing virtio descriptors, it does following operations:
Determine the number of descriptors available by polling on virt queue notification address.
Issue DMA using
DPDK DMA libraryto copy the descriptors to shadow queues.Pre-allocate mbufs for actual packet data. Worker cores checks the shadow queue for the available descriptors and issue DMA for actual packet data using these mbufs.
Fetch all DMA completions.
Mark used virtio descriptors as used in Host descriptor memory.
The dao_virtio_net_desc_manage() API is used to manage the virtio descriptors.
Application is expected to call this from a service core as frequently
as possible to shadow descriptors between Host and DPU memory.
dao_virtio_net_desc_manage(uint16_t dev_id, uint16_t qp_count);
The parameter qp_count specifies the active virt queue pair count. Below is the sample code to get qp_count.
virt_q_count = dao_virtio_netdev_queue_count(virtio_devid);
qp_count = virt_q_count/2;
14.10. Enqueue Burst API#
The burst enqueue API, enqueues the packet buffers to the host. It uses virtio net device identifier
and host Rx virt queue identifier to schedule the processing on. The nb_mbufs parameter is the
number of operations to process which are supplied in the mbufs array of rte_mbuf structures.
The enqueue function returns the number of operations it actually enqueued for processing. This API
is expected to execute by worker cores.
uint16_t dao_virtio_net_enqueue_burst(uint16_t devid, uint16_t qid,
struct rte_mbuf **mbufs, uint16_t nb_mbufs)
Enqueueing includes following operations:
Adds
virtio_net_hdrto the supplied mbuf’s packet data.Prepares the descriptors and DMA of descriptors to the host RX queue.
14.11. Dequeue Burst API#
The dequeue API, dequeues the packet buffers from the host. It uses the same format as the enqueue
API of processed but the nb_mbufs and mbufs parameters are now used to specify the max
processed operations the user wishes to retrieve and the location in which to store them.
The API call returns the actual number of processed operations returned, this can never be larger
than nb_mbufs.
uint16_t dao_virtio_net_dequeue_burst(uint16_t devid, uint16_t qid,
struct rte_mbuf **mbufs, uint16_t nb_mbufs)
Dequeueing includes following operations:
Issue DMAs for mbufs.
Fetch dma status and update the shadow mbuf offset, so that service core can mark the descriptors as used based on the shadow mbuf offset.
