15. RDMA Solution#
15.1. RDMA Overview#
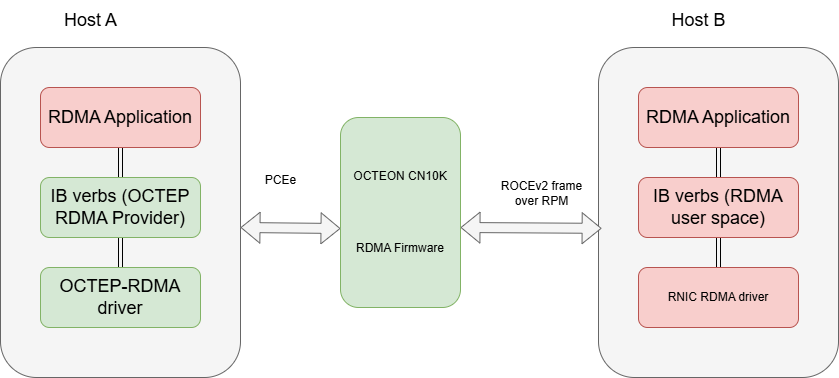
Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) enables zero-copy data transfer between memory regions of two systems without CPU involvement in the data path. This significantly reduces latency and CPU overhead, making RDMA ideal for high-performance networking.
RoCE v2 (RDMA over Converged Ethernet v2) encapsulates RDMA traffic over UDP/IP, allowing it to be routable across Layer 3 networks.
RDMA solution comprises multiple software components working together: on the x86 host, the rdma-core user-space libraries and kernel modules provide RDMA verbs and core functionality, while on the Octeon CN10K, a DPDK-based firmware application maintains RDMA resource contexts and performs RoCEv2 encapsulation for high-performance data transfer
15.2. Octeon RDMA Firmware#
dao-rdma_graph (referred to here as rdma) is a DPDK based application
that exercises RDMA (RoCEv2/IB verbs) dataplane paths on OCTEON and host
platforms. It supports multi-queue (multi-QP) UD and RC transports,
multi-device scenarios (multiple RDMA interfaces), and validation via
standard rdma-core utilities (ibv_*) and RDMA perftests utilities.
The application configures required RPM/SDP/DPI resources on OCTEON, launches
workers to process Ethernet receive nodes feeding RDMA graph nodes, and allows
users to run verbs test programs (ibv_ud_pingpong, ibv_ud_mq_trf,
ibv_rdma_mq_trf) across host <-> OCTEON or multi-device setups.
15.2.1. Features#
DPDK based RDMA dataplane orchestration on OCTEON (RPM + SDP + DPI VFs)
Supports UD transport ping/pong validation (
ibv_ud_pingpong)Supports multi-queue UD and RC tests (
ibv_ud_mq_trf,ibv_rdma_mq_trf)Multi-device RDMA support (multiple RDMA VF devices)
Works with host-side
rdma-coreutilities for probing & statsVFIO-PCI binding for RPM/SDP/DPI devices
Programmable number of Queue Pairs (QPs) per test
Command-line options for selecting device masks, number of RDMA devices, etc.
Integrates with perftest utilities (
ib_send_lat,ib_send_bw,ib_write_lat,ib_write_bw,ib_read_lat,ib_read_bw) for latency & bandwidth benchmarkingSupports high-performance RDMA memory allocations and multi-QP resource scaling
15.2.2. Setting up Environment#
Bind RPM device to vfio-pci:
dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci 0002:02:00.0
# Additional RPM PF (example latest FW):
dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci 0002:18:00.0
Bind SDP device (BDF may differ on older FW):
dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci 0002:01:00.1
# Old FW example: 0002:1f:00.1
If using older FW image requiring revert:
# Revert commit affecting SDP port-id 0 handling
git revert 4daa27051d79342f73916c17d9c5e37293848211
PEM setup (bind platform devices):
pem_sfx="pem0-bar4-mem"
sdp_sfx="dpi_sdp_regs"
for dev_path in /sys/bus/platform/devices/*; do
if [[ -d "$dev_path" && "$dev_path" =~ $pem_sfx || "$dev_path" =~ $sdp_sfx ]]; then
dev_name=$(basename "$dev_path")
echo "vfio-platform" > "$dev_path/driver_override"
echo "$dev_name" > /sys/bus/platform/drivers/vfio-platform/bind
echo "Device $dev_name configured."
fi
done
Enable and bind DPI/NPA devices (sample script dpi-test-setup.sh):
NUM_DPI=1
NUMVFS=12
DPIPF=$(lspci -d 177d:a080 | awk '{print $1}' | head -${NUM_DPI})
mkdir -p /dev/huge
mount -t hugetlbfs nodev /dev/huge
echo 12 > /sys/kernel/mm/hugepages/hugepages-524288kB/nr_hugepages
for PF in $DPIPF; do
DPIVFS=$(cat /sys/bus/pci/devices/$PF/sriov_numvfs)
if [ "x$DPIVFS" != x"$NUMVFS" ]; then
TOTALVFS=$(cat /sys/bus/pci/devices/$PF/sriov_totalvfs)
[ $TOTALVFS -lt $NUMVFS ] && NUMVFS=$TOTALVFS
echo 0 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/$PF/sriov_numvfs
echo $NUMVFS > /sys/bus/pci/devices/$PF/sriov_numvfs
fi
done
DPIVF=$(lspci -d 177d:a081 | awk '{print $1}')
NPAPF=$(lspci -d 177d:a0fb | awk '{print $1}' | head -1)
for DEV in ${DPIVF} $NPAPF; do
if [ -e /sys/bus/pci/devices/$DEV/driver/unbind ]; then
drv=$(basename $(readlink -f /sys/bus/pci/devices/$DEV/driver))
[ "$drv" != "vfio-pci" ] && echo $DEV > /sys/bus/pci/devices/$DEV/driver/unbind
fi
echo vfio-pci > /sys/bus/pci/devices/$DEV/driver_override
echo $DEV > /sys/bus/pci/drivers_probe
done
Latest SDK firmware extra binding (if needed):
echo vfio-pci > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0002:18:00.0/driver_override
echo 0002:18:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers_probe
Obtain DAO sources and checkout RDMA branch:
git clone https://sj1git1.cavium.com/IP/SW/dataplane/dpu-offload
cd dpu-offload
git checkout rdma-core-57.0-devel
15.2.2.1. Cross Compile for ARM64:#
Follow: https://marvellembeddedprocessors.github.io/dao/guides/gsg/build.html#compiling-and-installing
15.2.3. Launching RDMA Application on OCTEON#
Export DPI device list and run application:
export DPI_DEV="-a 0000:06:00.1 -a 0000:06:00.2 -a 0000:06:00.3 -a 0000:06:00.4 -a 0000:06:00.5 -a 0000:06:00.6 \
-a 0000:06:00.7 -a 0000:06:01.0 -a 0000:06:01.1 -a 0000:06:01.2 -a 0000:06:01.3 -a 0000:06:01.4 -a 0000:06:01.5"
cd <PATH TO DPU-OFFLOAD>/dpu-offload/build/app
./dao-rdma_graph -c 0x1f -a 0002:02:00.0 -a 0002:01:00.1 $DPI_DEV --file-prefix=ep -- -p 0x3 -P
Sample boot log excerpt:
[lcore -1] DAO_INFO: RDMA application version 25.01.0-24.11.0-d6645f1
EAL: Detected CPU lcores: 24
...
[lcore 0] DAO_INFO: Port 0 Link up at 100 Gbps FDX Fixed
[lcore 0] DAO_INFO: Port 1 Link up at 100 Gbps FDX Autoneg
[lcore 0] DAO_INFO: Setting up 8 VFs for PEM0
[lcore 0] DAO_ERR: No rings configured per VF, host interrupts unsupported
[lcore 0] DAO_INFO: graph node: rdma_eth_rx-0-0
[lcore 0] DAO_INFO: graph node: rdma_eth_rx-0-1
[lcore 0] DAO_INFO: graph node: rdma_eth_rx-1-0
[lcore 0] DAO_INFO: graph node: rdma_eth_rx-1-1
[lcore 0] DAO_INFO: Launching worker loops....
Note
Ensure that the Octeon CN10K firmware is fully initialized and running before configuring the RDMA software components on the host.
15.3. Host Software Architecture#
The host initiates RDMA communication using the RDMA verbs API provided by rdma-core.
15.3.1. a. User Space#
Application: Uses RDMA verbs (e.g., ibv_post_send, ibv_post_recv) through libibverbs.
rdma-core: Provides libraries and utilities for RDMA (e.g., libibverbs, libmlx5, etc.).
Includes vendor-specific provider implementation (e.g., Mellanox, Broadcom, Marvell CNXK). Provider translates generic verbs into hardware-specific operations.
15.3.2. b. Kernel Space#
ib_core: RDMA core kernel module providing common RDMA infrastructure.
Vendor-specific kernel driver: Implements low-level hardware interaction for the RDMA adaptor.
Handles Queue Pairs (QPs), Completion Queues (CQs), memory registration, and DMA mapping.
15.3.3. Setting up Environment#
Clone DAO sources for host kernel driver:
git clone https://github.com/MarvellEmbeddedProcessors/dao.git
cd dao
git checkout dao-devel
Build DAO for x86 host
rdma-core is defined as a subproject, kernel header updates and its compilation
will be handled with following instructions.
Note
Meson version 1.8.0 or higher is mandatory for RDMA host build.
Update meson version on host to >= 1.8.0 using following command:
pip3 install meson==1.8.0
meson setup build -Dkernel_dir=KERNEL_BUILD_DIR -Drdma_build=true
Eg.
ninja -C build
# Module at build/kmod/rdma/octep_rdma/octep-rdma.ko
Insert module & dependencies (ensure Octeon FW running):
modprobe ib_uverbs
insmod build/kmod/rdma/octep_rdma/octep-rdma.ko
Validate device probing:
./build/bin/ibv_devices
./build/bin/ibv_devinfo
Bring up host interface:
ifconfig enp1s0 30.0.0.3 up
Partner Machine Setup (MLX example):
/etc/init.d/openibd restart
ifconfig enp6s0f1np1 30.0.0.11
ping 30.0.0.3
rdma link show
ibv_devices
ibv_devinfo
15.3.4. UD Ping-Pong Test#
Server (partner MLX device):
ibv_ud_pingpong -g 3 -d mlx5_1 -i 1
Client (host with octep driver):
./build/bin/ibv_ud_pingpong -g 1 -d octep_rdma_0 -i 1 30.0.0.11
Successful output example (server/client throughput & latency lines retained).
15.3.5. Multi-Queue UD Test (ibv_ud_mq_trf)#
Clone & build rdma-core (both sides) if not already done. Launch server:
./build/bin/ibv_ud_mq_trf -g 1 -q 1 -s
Flags:
-g <idx>GID index-q <num>Number of QPs (increase to stress multi-queue, e.g.-q 4)-sServer mode
Client example:
./build/bin/ibv_ud_mq_trf -g 1 -q 1 -r 20.20.20.21
15.3.6. Multi-Device RDMA Steps#
Create RPM VFs and bind to VFIO-PCI:
echo 0002:02:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/vfio-pci/unbind
echo > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0002:02:00.0/driver_override
echo 0002:02:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/rvu_nicpf/bind
echo 3 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0002:02:00.0/sriov_numvfs
dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci 0002:02:00.1
dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci 0002:02:00.2
dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci 0002:02:00.3
Bind SDP VFs:
dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci 0002:1f:00.1
dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci 0002:1f:00.2
dpdk-devbind.py -b vfio-pci 0002:1f:00.3
Start application for 3 devices:
dao-rdma_graph -c 0x1f -a 0002:02:00.1 -a 0002:02:00.2 -a 0002:02:00.3 -a 0002:1f:00.2 -a 0002:1f:00.3 -a 0002:1f:00.4 $DPI_DEV --file-prefix=ep -- -p 0x3F -r 0x7 -n 3 -P
-nNumber of RDMA devices-rRDMA devices mask
Insert module & create RDMA VFs on host:
insmod build/kmod/rdma/octep_rdma/octep-rdma.ko
echo 3 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:01:00.0/sriov_numvfs
Verify IB devices:
./build/bin/ibv_devices
Configure VF interfaces (examples):
ifconfig enp1s0v0 30.0.0.1
ifconfig enp1s0v1 31.0.0.1
ifconfig enp1s0v2 32.0.0.1
Check GIDs:
./build/bin/ibv_devinfo -v
Partner device RPM VFs & RXE configuration:
echo 3 > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0002:02:00.0/sriov_numvfs
ifconfig enP2p2s0v0 30.0.0.2
ifconfig enP2p2s0v1 31.0.0.2
ifconfig enP2p2s0v2 32.0.0.2
rdma link add rxe1 type rxe netdev enP2p2s0v0
rdma link add rxe2 type rxe netdev enP2p2s0v1
rdma link add rxe3 type rxe netdev enP2p2s0v2
15.3.6.1. Connectivity validation (ping multiple IPs)#
Perform ICMP pings to each partner VF IP to ensure reachability.
15.3.6.2. Multi-Device UD Ping-Pong Examples#
Partner:
./build/bin/ibv_ud_pingpong -g 1 -d rxe1 -i 1
Host:
./build/bin/ibv_ud_pingpong -g 1 -d octep_rdma_1 -i 1 30.0.0.2
15.3.7. Troubleshooting#
If ibv_ud_pingpong shows empty GID (GID ::):
IP likely not configured on interface; assign IP and re-check.
Kernel log may show:
octep_rdma 0000:01:00.0: Invalid MSIX entry 0 for Q-1If IPv6 GID appears unexpectedly, try different
-gindex (e.g.-g 2or-g 1).
15.3.8. Command-Line Scenarios (Multi-QP Application)#
Single Server / Single Client, 1000 QPs, SGE=1
Server:
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -q 1000 -t 8
Client UD Mode:
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -g <gid-idx> -q 1000 -t 8 -d <device-name> --qp-type UD --op-type SEND -n <iters> <server-ip>
Client RC Examples:
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -g <gid-idx> -q 1000 -t 8 -d <device-name> --qp-type RC --op-type SEND -n 10 --size 1024 <server-ip>
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -g <gid-idx> -q 1000 -t 8 -d <device-name> --qp-type RC --op-type WRITE -n 10 --size 1024 <server-ip>
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -g <gid-idx> -q 1000 -t 8 -d <device-name> --qp-type RC --op-type WRITE_IMM -n 10 --size 1024 <server-ip>
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -g <gid-idx> -q 1000 -t 8 -d <device-name> --qp-type RC --op-type READ -n 10 --size 1024 <server-ip>
Single Server / Single Client, 1000 QPs, SGE=2
Server:
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -q 1000 -t 8 --nb-sge=2
Client UD Mode:
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -g <gid-idx> -q 1000 -t 8 -d <device-name> --qp-type UD --op-type SEND -n <iters> --nb-sge=2 <server-ip>
Client RC Modes (SEND/WRITE/WRITE_IMM/READ) add --nb-sge=2 similarly.
Single Server with 1000 Clients, 1 QP Each, SGE=1
Server:
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -q 1 -t 8 -c 1000
Client Loops (example UD):
count=1
while [ $count -le 1000 ]; do
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -g <gid-idx> -q 1 -t 1 -d <device-name> --qp-type UD --op-type SEND -n <iters> <server-ip>
((count++))
done
For RC (SEND/WRITE/WRITE_IMM/READ) run separate loops (example count up to 250 each) as in reference steps.
Single Server with 1000 Clients, 1 QP Each, SGE=2
Server:
./build/bin/ibv_rdma_mq_trf -q 1 -t 8 -c 1000 --nb-sge=2
Client UD / RC loops similar to SGE=1 case adding --nb-sge=2.
15.3.9. Planned Enhancements#
Extended statistics and graphs for RDMA nodes
Automated multi-QP stress scripts
IPv6 focused examples
Integration with perf benchmarks
15.3.10. Known Issues#
Empty GID requires manual IP configuration or correct GID index selection
Some platform device probes may fail harmlessly (logged) depending on FW
Multi-device setups rely on correct VF ordering; mismatches can cause mask errors
15.3.11. References#
rdma-core upstream documentation
OCTEON SDK Getting Started Guide
DPDK Programmer’s Guide (EAL & VFIO binding)
15.3.12. Performance Testing (Perftest Suite)#
The RDMA application supports standard perftest tools for exercising latency,
bandwidth, and operation-specific performance over both UD and RC transports.
Below are generalized usage patterns using devices like octep_rdma_0
and a partner Mellanox device (e.g. mlx5_1). Adjust GID indices, IPs,
queue counts (-q), iteration counts (-n), and operation modes as
appropriate for your environment.
- General Notes:
Run server side commands (those without a destination IP) on the responder host.
Client side adds destination IP (last argument) to initiate connection.
Use
--gid-index <idx>to select RoCE v2 GID matching configured IP.-c UDselects Unreliable Datagram;-c RCselects Reliable Connected.-Fenables “Formatted” output;--report_gbitsreports throughput in Gbit/s.Increase
-q(number of QPs) to evaluate scalability; increase-nto extend test iterations.For read tests,
-o <order>may select posting order or opcode variant (per perftest help).
15.3.13. Latency Tests (UD / RC):#
Server examples (no destination IP):
ib_send_lat -d octep_rdma_0 -c UD -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a
ib_send_lat -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a
ib_write_lat -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a -n 40
ib_read_lat -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a -o 2
Client counterparts (add server IP):
ib_send_lat -d octep_rdma_0 -c UD -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a 20.10.10.3
ib_send_lat -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a 20.10.10.3
ib_write_lat -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a 20.10.10.3 -n 40
ib_read_lat -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a 20.10.10.3 -o 2
ib_read_lat -d mlx5_1 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 3 -F -a -o 2 20.10.10.2
15.3.14. Bandwidth Tests (UD / RC SEND, WRITE, READ):#
Server-side examples:
ib_send_bw -d octep_rdma_0 -c UD -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a -n 5 -q 15
ib_send_bw -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a -n 5 -q 2
ib_write_bw -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a -n 10 -q 2
ib_read_bw -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a -n 10 -q 2 -o 2
Client examples (add destination IP):
ib_send_bw -d octep_rdma_0 -c UD -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a 20.10.10.3
ib_send_bw -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a -n 5 -q 10 20.10.10.3
ib_write_bw -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a -n 10 -q 10 20.10.10.3
ib_write_bw -d mlx5_1 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 3 -F -a -q 2 -n 10 20.10.10.2
ib_read_bw -d octep_rdma_0 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 1 -F --report_gbits -a -n 10 -q 2 -o 2 20.10.10.3
ib_read_bw -d mlx5_1 -c RC -i 1 --gid-index 3 -F -a -q 2 -n 10 -o 2 20.10.10.2
- Scaling Guidelines:
Increase
-qto test parallel QPs for throughput scaling (e.g. 2, 10, 15).Adjust
-niterations for longer measurement windows (latency stabilization).Use consistent MTU settings across devices (verify with
ibv_devinfo).Ensure GID indices map to the IPv4-mapped RoCE v2 addresses (
::ffff:X.Y.Z.W).Validate link status and speed before benchmarking.
- Memory Allocation Considerations:
Pre-allocate large buffers to avoid page faults during measurement.
Pin hugepages if using user-space memory registration for stable results.
Reuse registered MR across QPs when possible to reduce setup overhead.
- Result Interpretation:
Latency outputs typically include min/avg/max; track jitter when increasing QPs.
Bandwidth tests report Gbit/s; correlate with line rate (e.g. 100G) and packet size.
For WRITE/READ, consider PCIe round-trip and completion queue depth effects.
- Troubleshooting Perftest:
Empty or incorrect GID: re-check IP assignment or use alternate
--gid-index.Low bandwidth: verify flow control settings, MTU, and absence of packet drops (
ethtool -S).Elevated latency spikes: inspect CPU frequency scaling, NUMA placement, and interrupt affinity.
